Sofosbuvir is a revolutionary antiviral medication used primarily for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Since its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2013, it has transformed HCV treatment, offering high cure rates with fewer side effects compared to older therapies. This article provides a comprehensive overview of sofosbuvir, including its uses, benefits, side effects, dosage guidelines, warnings, and other essential information.
What Is Sofosbuvir?
Sofosbuvir is a direct-acting antiviral (DAA) drug that inhibits the replication of the hepatitis C virus. It works by blocking the action of the HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, an enzyme essential for viral replication. Sofosbuvir is often used in combination with other antiviral medications, such as ledipasvir, velpatasvir, or daclatasvir, to enhance its effectiveness.
Brand Names
Sofosbuvir is sold under various brand names, including:
- Sovaldi (sofosbuvir alone)
- Harvoni (sofosbuvir + ledipasvir)
- Epclusa (sofosbuvir + velpatasvir)
- Vosevi (sofosbuvir + velpatasvir + voxilaprevir)
Uses of Sofosbuvir
Sofosbuvir is primarily prescribed for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection in adults and children (aged 3 years and older). It is effective against multiple HCV genotypes, making it a versatile treatment option.
1. Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection
Sofosbuvir is used to treat all six major genotypes of HCV, either as a standalone drug (in combination with ribavirin) or as part of a fixed-dose combination (e.g., with ledipasvir or velpatasvir).
2. Combination Therapy for Higher Efficacy
Since HCV can develop resistance to single-drug therapy, sofosbuvir is often combined with other antivirals to improve cure rates. Common combinations include:
- Sofosbuvir + Ledipasvir (for genotypes 1, 4, 5, and 6)
- Sofosbuvir + Velpatasvir (for all genotypes, including 1-6)
- Sofosbuvir + Daclatasvir (commonly used in resource-limited settings)
- Sofosbuvir + Ribavirin (for genotypes 2 and 3)
3. Treatment for Patients with Liver Cirrhosis or HIV Coinfection
Sofosbuvir-based regimens are effective even in patients with advanced liver disease (compensated cirrhosis) and those coinfected with HIV.
Benefits of Sofosbuvir
The introduction of sofosbuvir has revolutionized HCV treatment due to its numerous advantages:
1. High Cure Rates (Over 90%)
Unlike older interferon-based therapies, sofosbuvir-based treatments achieve sustained virologic response (SVR) rates exceeding 90%, meaning the virus is undetectable in the blood months after treatment.
2. Shorter Treatment Duration
Traditional HCV treatments required 24-48 weeks, whereas sofosbuvir-based regimens often last 8-12 weeks, improving patient compliance.
3. Fewer Side Effects
Interferon-based therapies caused severe side effects (fatigue, depression, flu-like symptoms). Sofosbuvir is better tolerated, with milder adverse effects.
4. Oral Administration
Sofosbuvir is taken as a once-daily pill, eliminating the need for painful injections.
5. Effective for Hard-to-Treat Cases
It works well in patients with:
- Liver cirrhosis
- HIV coinfection
- Previous treatment failures
Side Effects of Sofosbuvir
While sofosbuvir is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects.
Common Side Effects
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Weakness
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate) – when used with amiodarone (a heart medication)
- Hepatitis B reactivation – in patients with past HBV infection
- Allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage
- Standard dose: 400 mg once daily (with or without food)
- Combination therapy: Depends on the accompanying drug (e.g., ledipasvir 90 mg + sofosbuvir 400 mg in Harvoni)
Treatment Duration
- Genotypes 1, 4, 5, 6: 12 weeks (may extend to 24 weeks in cirrhosis)
- Genotypes 2 & 3: 12 weeks (sometimes with ribavirin)
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered unless it’s close to the next dose. Do not double the dose.
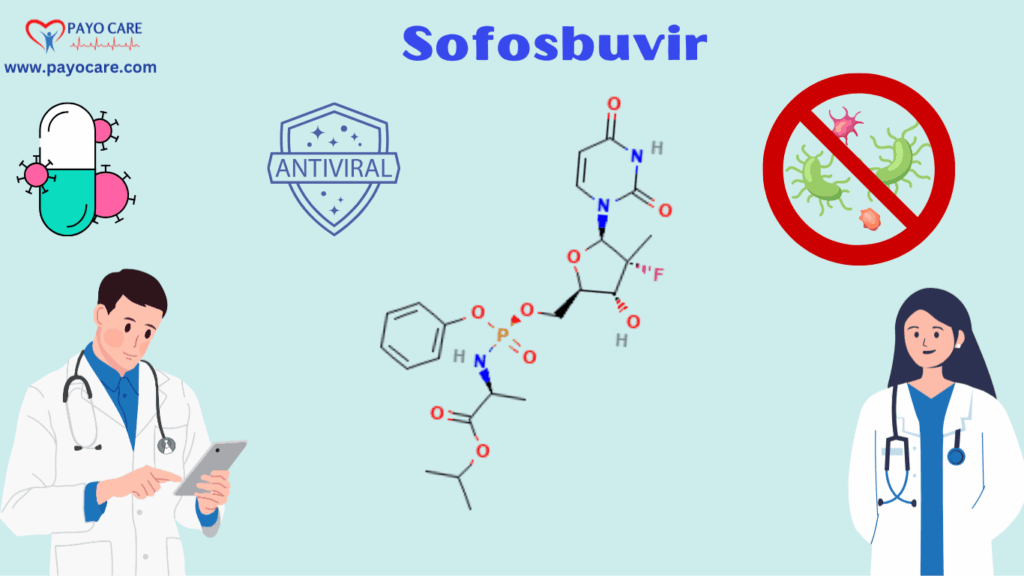
Warnings and Precautions
1. Hepatitis B Reactivation
Patients with past HBV infection should be monitored, as sofosbuvir can reactivate hepatitis B.
2. Drug Interactions
Sofosbuvir interacts with:
- Amiodarone (risk of severe bradycardia)
- Rifampin, St. John’s wort (decreases sofosbuvir effectiveness)
- Antacids, PPIs (may reduce absorption; take 4 hours apart)
3. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy: Safety not fully established; ribavirin (if used in combination) is teratogenic.
- Breastfeeding: Unknown if sofosbuvir passes into breast milk; consult a doctor.
4. Kidney and Liver Impairment
- Severe kidney disease: Use with caution (dose adjustment may be needed).
- Decompensated cirrhosis: Avoid certain combinations (e.g., sofosbuvir + velpatasvir + voxilaprevir).
Conclusion
Sofosbuvir has transformed hepatitis C treatment, offering high cure rates, shorter therapy duration, and fewer side effects compared to older treatments. While generally safe, patients should be aware of potential drug interactions and side effects. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting treatment to ensure the best outcomes.
With ongoing advancements, sofosbuvir continues to play a crucial role in the global fight against hepatitis C, bringing hope to millions of patients worldwide.
References
- FDA Prescribing Information for Sovaldi.
- World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines for HCV Treatment.
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) Recommendations.
10 FAQs on Sofosbuvir
1. What is Sofosbuvir used for?
Sofosbuvir is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, often in combination with other drugs like ledipasvir or daclatasvir.
2. How does Sofosbuvir work?
It inhibits the HCV RNA polymerase enzyme, preventing the virus from replicating and reducing viral load in the body.
3. What are the common side effects of Sofosbuvir?
Common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia, and mild rash. Severe side effects are rare but may include bradycardia (slow heart rate) when taken with amiodarone.
4. What is the recommended dosage of Sofosbuvir?
The typical dose is 400 mg once daily, taken with or without food, usually for 12 to 24 weeks, depending on the HCV genotype and combination therapy.
5. Can Sofosbuvir cure hepatitis C?
Yes, when used in combination with other antivirals, Sofosbuvir has a high cure rate (over 90%) for hepatitis C.
6. Who should not take Sofosbuvir?
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (unless prescribed)
- Patients with severe kidney disease (without dose adjustment)
- Those allergic to Sofosbuvir or its components
7. Does Sofosbuvir interact with other medications?
Yes, it may interact with:
- Amiodarone (risk of severe bradycardia)
- Rifampin, St. John’s wort (reduces effectiveness)
- Certain HIV medications (consult a doctor)
8. Is Sofosbuvir safe for liver cirrhosis patients?
Yes, it is effective for HCV patients with compensated cirrhosis but should be used cautiously in decompensated cases (may require adjusted therapy).
9. How long does it take for Sofosbuvir to work?
Most patients see a significant reduction in viral load within 4-12 weeks, with full results after completing the treatment course.
10. Is Sofosbuvir available as a generic drug?
Yes, generic versions are available and are more affordable than the brand-name drug (Sovaldi).